The Coronavirus Covid-19 outbreak has spread rapidly in various parts of the world, where it has affected not only people in health but also in economic matters.
In the short term, the industries that will be most affected are entertainment, tourist services, and accommodation; they will have the first effects in the face of this crisis and in the medium term the manufacturing industry, such as the foods and beverages industry.
Practically 58 percent of the people who work in our country do so in the informal sector, in such a way that they will see their activity suffer in upcoming days.
Many countries have closed their borders and asked their citizens to stay at home in order to curb contagion, but this measure has greatly affected both small and medium-sized food and beverage companies.

Months of uncertainty, difficulties, and economic slowdown are approaching worldwide due to this contingency. The “quarantine” in which much of society is in order to lower the contagion is already generating a strong impact on sales and in a short time, it will also do so on production and employment.
A survey carried out among 788 independent entrepreneurs and professionals of food and beverage companies from all over the country revealed that 58% are suffering a drop in sales, 40% in purchases; 39% in production, and 33% in occupancy levels. The main recorded negative impact is on sales. The other three impacts are much less widespread, but these proportions are sure to change in the coming weeks, as lower sales will negatively affect production and employment.
The ability of smaller companies to accumulate stocks on deposit is limited, even more so under current financial conditions. On the other hand, the evolution of the problem with purchases will depend on the degree of internationalization of the supply chain of each SME. For the moment, the negative impact on sales is more important in commerce than in services and manufacturing.
The alcoholic beverage industry today faces serious challenges. Generally, the tourism sector is one of the major pillars of the sale of alcoholic beverages in most countries. Today, they are under serious threat due to the Covid-19 pandemic, which limits outdoor activities in order to minimize the risk of the virus spreading. Bars and restaurants are no longer frequented, consumption is mainly in homes but still remains relatively low.
Also, the drop in economic activity and consumer purchasing power during this period of crisis negatively impacted the demand for alcoholic beverages. In addition, since the purchases of these products are now made only through retail channels (markets, supermarkets, convenience stores, etc.), the sums spent by consumers are less important than through the tourism circuit, and this will greatly impact the turnover of the sector.
As in other countries, many consumers save money and buy only the most basic and essential food items; they ignore wines and spirits which are considered luxury products. The demand, greatly reduced, is still present. Importers and distributors are developing e-commerce and home delivery.
In this context, the import volume of beverages will certainly decrease. Locally, the factories of Heineken and Carlsberg Brewery did not obtain government authorization to continue making beers during the containment period.
Regarding imports of beverages from the country, a decrease of 35 to 40% is estimated for the year 2020.
The food industry has been hit. The pandemic has restricted traveling to your favorite restaurant. Most of these restaurants are own by the middle class who are trying to make a name for themselves. The workers in these restaurants are part of the lower wage class and immigrants. The closure of businesses means they are left without a paycheck and do not have the necessary skills to work from home.
As for the hotels, they are almost all closed due to the absence of tourists. The impact is therefore considerable for sales of beverages and foods among tourists/travelers in the tourism sector. However, an increase in sales via retail channels is observed, as many people now buy and consume foods and beverages at home. Online sales are also growing in this context, with importers/distributors who offer free deliveries and take advantage of social networks, such as Facebook and Instagram.
In Contra Costa California, we are finding that 80% of businesses are microbusinesses employing under 10 employees. We know that these businesses also have a limited cash reserve and are not in a position to take on more debt, especially with landlords collecting rent. Many of these microbusinesses are sole proprietorships and are minority-owned which rely on the general public to keep them afloat. One of the bigger issues at this time is that the employees of the small businesses are hesitant to return to work for safety concerns (which then ties in health insurance stuff) and at the same time they do not want to return because of the unemployment checks that may be greater than their salary.
The workers are also stuck in a place where they do not have childcare resources if they return to work.
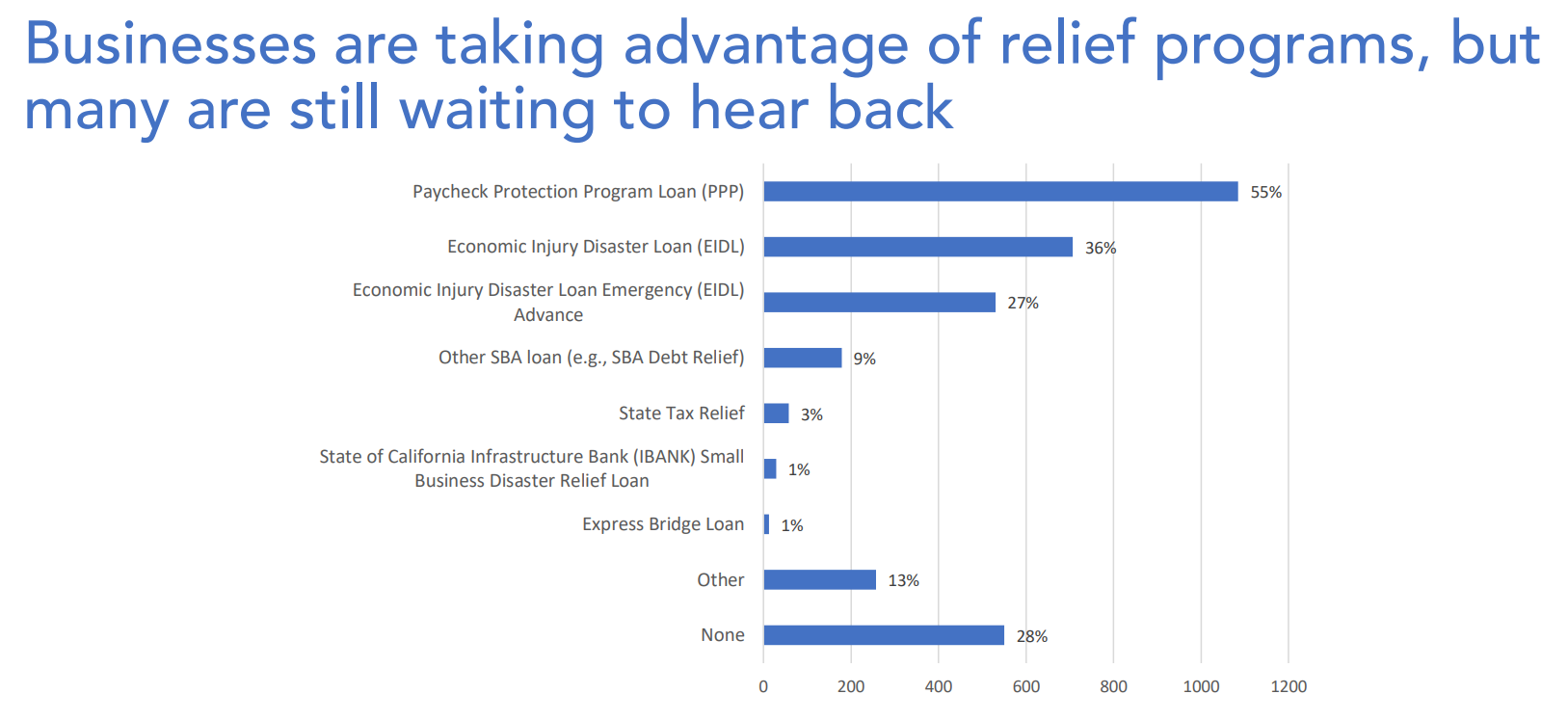
Just to help define what microbusinesses are, they are small businesses that are owned by a minority with under 10 employees. Currently, the relief programs are slow in providing
What are the immediate measures to be taken into account by microbusinesses in the queue of this Covid-19 pandemic?
Without a doubt, it can be agreed that maintaining a healthy financial flow (for example, liquidity) is one of the main points, the other is to design and define a prompt, coordinated, and effective response to each of those involved. Stakeholders’ functions should be shared according to the role and expectations of each one, as well as the obligations that have in the field of the company in question and the duty to be and avoid the loss and lack of attention to incentives in all moment. Another important point is that, on the one hand, you must understand the depth and impact of the crisis, but without forgetting that you must be prepared for when you go through the end of it at all times.
If you are lucky enough, you have a personalized business that can serve people over the internet. We have seen many cases where yoga instructors, consultants, lawyers, and tax accountants have continued on with business and conducting their business over web conferencing.
If you have a business that still requires you to work, or one where you can make deliveries easily by vehicle, you need to exercise caution now more than ever. Avoid reckless behavior that could affect your business, a DUI is not what you need right now. While you might be able to apply for a hardship license if your livelihood would be impacted by being banned from driving, you should do what you can to avoid trouble in the first place. Stick to guidelines and be strict with health and safety to help you keep your business afloat at this difficult time.
What are the main mistakes of microbusinesses during this Covid-19 pandemic?
One of the most common mistakes is not giving yourself the opportunity to understand the context and nature of the crisis and therefore its scope, this implies the impossibility of preparing for something that is not understood. You cannot lose focus and for this, it is necessary to make an evaluation on the one hand of what is the purpose of the company and what its business model implies. On the other hand, it is also important to understand what risks it brings to operational, financial, relational continuity, etc. the crisis itself but also what opportunities the situation might bring. Many times, we want to continue “operations as usual”, ignoring the possibility of adaptation and innovation among others that the situation presents. For example, if it applies that my business model at the point of sale is compromised, it would be necessary to see what opportunities for buying and selling through the internet or mobile means, even logistics and consumer experience, could be adapted and applied. It is necessary to promote business models as far as possible that present flexibility to adapt to present circumstances but also to future ones. From the adoption of technologies to processes based on them.
Much is said about digital transformation, for example, here the issue is that society is already immersed in it, and many businesses are not in a position or have not understood the opportunities that the same partially or more comprehensively could propose or support within their processes and business potential. The issue is not to paralyze the business, but to bias and recompose it. It is then that the concept of innovation becomes enormously relevant.
Conclusion
Not sure if there is a conclusion to all this but we know that this pandemic has affected many of the microbusinesses out there. If you can, support the small businesses. These are the businesses that are local to your city.
As we see more restrictions lifted we are now seeing another side of what business will look like in the future. The limits of people in a venue will lower revenue. We can assume that more businesses will try to find an online solution to continue.
For more information, visit East Bay Economic Development Alliance.